Air Pollution and Its Effects
Air pollution is a big problem that often people ignore. It leads to health problems, poor quality of life, and less productivity. Everyone is affected by poor air quality, but children, the elderly, and people with cardiovascular or respiratory problems are the ones that suffer the most with this problem. According to studies, air quality in Europe is below the recommended levels, making it even more important to have mechanisms in place to monitor air quality over time.
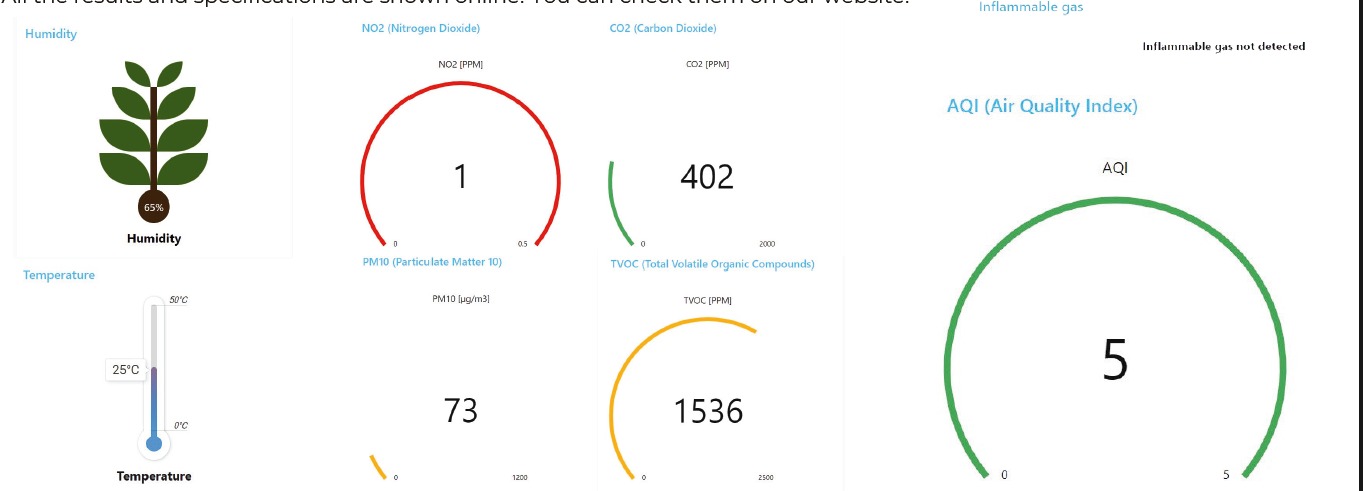
AQI (Air Quality Index)
AQI is an indicator used around the world by government agencies to rate how polluted the air is. The lower the AQI rate is, the more polluted the air is, and greater are the public air risks. Our AQI rating takes into account 4 parameters: CO2, NO2, TVOC, and PM10. The rating to the air is given based on the worst concentration of one of the 4 parameters:
- Rating 5 means that the air is clean;
- Rating 4 means that the air is acceptable, but extremely sensitive individuals may experience light symptoms;
- Rating 3 means that children, the elderly, and people with respiratory problems may experience adverse health effects;
- Rating 2 means more serious effects on the health of sensitive groups and possible effects on the health of the general population;
- Rating 1 means that the air quality is at dangerous levels, leading to very serious health effects to the entire population.
Parameters
CO2 (Carbon Dioxide)
Associated with climate change, CO2 is also a cause of the low levels of quality of the air. This gas gives a good indication of the rate of ventilation in an indoor room, i.e. if the CO2 levels are high, it means that the ventilation rate in that room is low, and that means that other air pollutants are accumulating in the air like CO2. This gas in excess causes problems to the nervous system and, according to a study made by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, leads to a decrease in people’s productivity. Normal CO2 levels are around 400 PPM.
NO2 (Nitrogen Dioxide)
NO2 is a highly toxic gas that primarily results from car combustion and industrial activity. The excess of this gas in the air can cause the weakening of lung function, the increase of the risk of respiratory diseases and the worsening of asthma symptoms. The normal concentrations of NO2 in urban areas range from 0.02 PPM to 0.1 PPM.
TVOC (Total Volatile Organic Compounds)
Total Volatile Organic Compounds (TVOC) represents the sum of all compounds with high vapor and low water solubility. These gases are emitted from various products, such as cigarettes, paints, disinfectants, cleaning agents, perfumes, etc. Not all VOCs are harmful, but due to the existence of various VOCs, TVOC is used to assess their presence in the air, without distinguishing the harmful ones from the others. Symptoms caused by high concentrations in the air of harmful VOCs include fatigue, dizziness, allergic skin reactions, headaches, and nausea. Long-term exposure to harmful VOCs may lead to health problems in the kidneys, liver, and nervous system, as well as causing cancer. Normal levels of TVOC in the air are around 100 PPB.
PM10 (Particulate Matter)
The last parameter is PM10, and it represents particulate matter with a diameter of 10 micrometers or less. These particles have various sources, including dust, vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and natural sources. PM10 can penetrate our respiratory system and cause serious health problems, especially to sensitive groups, like decreasing respiratory capacity, cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, and lung cancer. Normal levels of PM10 range from 10 to 20 µg/m³.