Software Specification Exercises: Hoare Logic (Selected Solutions)
Software Specification, MEIC @ IST, 2020/21
@jff https://joaoff.com1. Three-variable swap
$$ \scriptsize \begin{array}{l} \{ x=m \wedge y=n \}\\ t := x; \\ \{ x=m \wedge y=n \wedge t=x \}\\ x := y; \\ \{ x=y \wedge y=n \wedge t=x \}\\ y := t \\ \{ x=y \wedge y=x \wedge t=x \} \rightarrow\\ \{ x=n \wedge y=m \} \end{array} $$2. Two-variable swap
$$ \scriptsize \begin{array}{l} \{ x=m \wedge y=n \}\\ x := x+y; \\ \{ x=m+n \wedge y=n \}\\ y := x-y; \\ \{ x=m+n \wedge y=(m+n)-n \}\\ x := x-y \\ \{ x=(m+n)-((m+n)-n) \wedge y=(m+n)-n \} \rightarrow\\ \{ x=n \wedge y=m \} \end{array} $$3. Maintaining a property
$$ \scriptsize \begin{array}{l} \{ x = r + (y\times q) \}\\ r := r-y; \\ \{ x = (r-y) + (y\times q) \}\\ q := q+1 \\ \{ x = (r-y) + (y\times (q+1)) \} \rightarrow\\ \{ x = (r-y) + (y\times q) + y)) \} \rightarrow\\ \{ x = r + (y\times q) \}\\ \end{array} $$4. The maximum value
$$ \scriptsize \begin{array}{l} \{\,\,true\,\,\} \\ \texttt{if}\,\,\,x\ge y\,\,\,\texttt{then} \\ ~~~\{\,\,true \wedge x\ge y\,\,\} \\ ~~~~~~ m := x \\ ~~~\{\,\,true \wedge x\ge y \wedge m=x\,\,\} \rightarrow \{true \wedge x\ge y \wedge m=max(x, y)\,\,\} \\ \texttt{else} \\ ~~~\{\,\,true \wedge y\gt x\,\,\} \\ ~~~~~~ m := y \\ ~~~\{\,\,true \wedge y\gt x \wedge m=y\,\,\} \rightarrow \{true \wedge y\gt x \wedge m=max(x,y)\,\,\} \\ \{\,\,m = max(x, y)\,\,\} \end{array} $$Assume that for all $x$ and $y$ we have $x\ge y \rightarrow max(x,y)=x$
4. The maximum value
Derivation tree:

5. Adding one to the other
$$ \scriptsize \begin{array}{l} \{ x=m \wedge y=n \wedge 0\leq n \} \rightarrow \{ x+y=m+n \wedge 0\leq y \}\\ \texttt{while}\,\,0\lt y\,\,\texttt{do \{} \\ ~~\{ x+y=m+n \wedge 0\leq y \wedge 0\lt y\}\\ ~~~ x := x+1; \\ ~~\{ x+1+y=m+n \wedge 0\leq y \wedge 0\lt y\}\\ ~~~ y := y-1 \\ ~~\{ x+1+y-1=m+n \wedge 0\leq y \wedge 0\lt y\} \rightarrow\\ \{ x+y=m+n \wedge 0\leq y \}\\ \texttt{\}}\\ \{ x+y=m+n \wedge 0\leq y \wedge y\leq 0\} \rightarrow \{ x = m+n \} \end{array} $$6. Integer division
$$ \scriptsize \begin{array}{l} \{ A\gt 0 \wedge B\gt 0 \}\\ q := 0; \\ r := A; \\ \texttt{while}\,\,r\ge B\,\,\texttt{do \{} \\ ~~~ q := q+1; \\ ~~~ r := r-B \\ \texttt{\}}\\ \{ A = q\times B + r \,\,\wedge\,\, 0\le r \,\,\wedge\,\, r\lt B \} \end{array} $$Solution hint: use as invariant $A = q\times B + r \,\,\wedge\,\, 0\le r$
7. Factorial
$$ \scriptsize \begin{array}{l} \{ x \ge 0 \}\\ y := 1; \\ z := 0; \\ \texttt{while}\,\,z\neq x\,\,\texttt{do \{} \\ ~~~ z := z+1; \\ ~~~ y := y*z \\ \texttt{\}}\\ \{ z = x \,\wedge\, y=x! \} \end{array} $$Solution hint: use as invariant $y = z!$
8. Euclid's algorithm
$$ \scriptsize \begin{array}{l} \{ 0\lt M \,\wedge\, 0\lt N\}\\ x:=M;\,\,y:=N;\\ \texttt{while}\,\,x\neq y\,\,\texttt{do \{} \\ ~~~ \texttt{if}\,\,\,x\lt y\,\,\,\texttt{then} \\ ~~~~~~~~~ y := y-x \\ ~~~ \texttt{else} \\ ~~~~~~~~~ x := x-y \\ \texttt{\}}\\ \{ x = y = GCD(M,N) \} \end{array} $$Solution hint: use as invariant $GCD(x,y) = GCD(M,N)$
8. Euclid's algorithm
Derivation tree (part 1):

8. Euclid's algorithm
Derivation tree (part A):
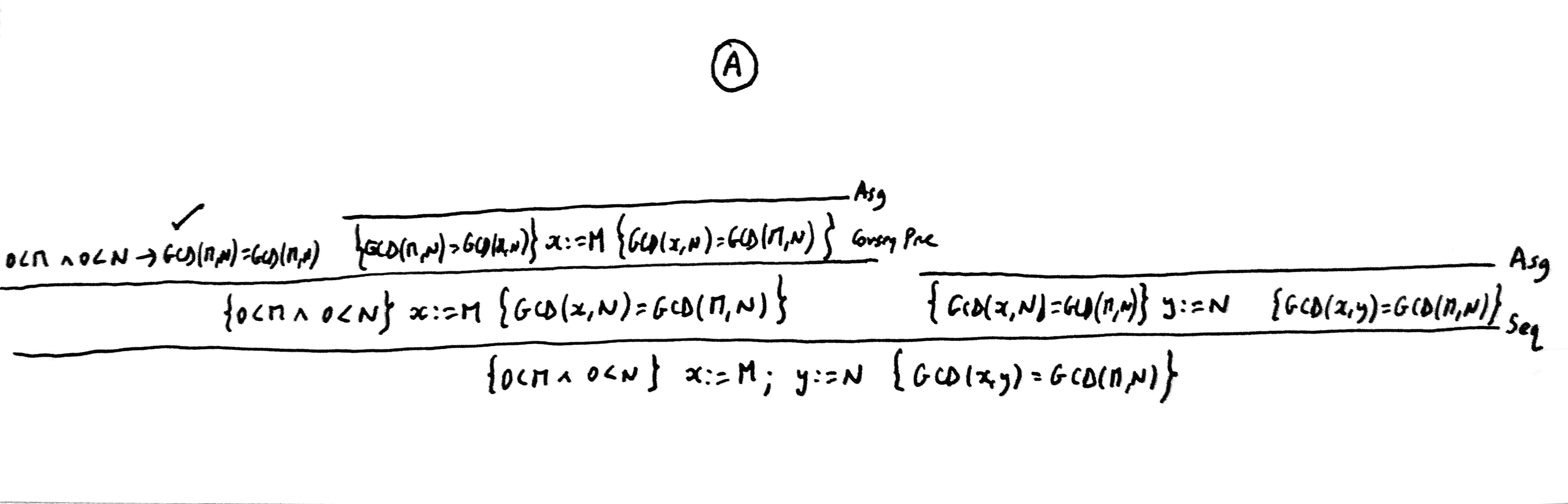
8. Euclid's algorithm
Derivation tree (part B):

9. Exponentiation
$$ \scriptsize \begin{array}{l} \{ A\ge 0 \,\wedge\, B\ge 0\}\\ r:=1;\,\,x:=0;\\ \texttt{while}\,\,x\neq B\,\,\texttt{do \{} \\ ~~~~~~ r := r*A; \\ ~~~~~~ x := x+1 \\ \texttt{\}}\\ \{ r = A^B \} \end{array} $$Solution hint: use as invariant $r = A^x$