Observer (padrão de desenho): Difference between revisions
From Wiki**3
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOCright}} | {{TOCright}} | ||
O padrão ''observer'' permite observar o estado de um objecto. Os observadores registam o seu interesse no estado junto do objecto; quando o estado do objecto muda, os observadores são notificados. | O padrão ''observer'' permite observar o estado de um objecto. Os observadores registam o seu interesse no estado junto do objecto; quando o estado do objecto muda, os observadores são notificados. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[Image:observer-dpcd.png|600px]] | [[Image:observer-dpcd.png|600px]] | ||
===Diagrama de | ===Diagrama de sequência=== | ||
As colaborações entre os intervenientes são as que figuram no seguinte diagrama de | As colaborações entre os intervenientes são as que figuram no seguinte diagrama de sequência: | ||
[[Image:observer-dpsd.png|500px]] | [[Image:observer-dpsd.png|500px]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
===Observadores e Observados=== | ===Observadores e Observados=== | ||
<java5> | |||
public interface Subject { | |||
public void registerObserver(Observer o); | |||
public void removeObserver(Observer o); | |||
public void notifyObservers(); | |||
} | } | ||
</java5> | |||
<java5> | |||
public interface Observer { | |||
public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure); | |||
} | } | ||
</java5> | |||
===Apresentação=== | ===Apresentação=== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 39: | ||
Esta interface define o método básico para apresentação de dados. | Esta interface define o método básico para apresentação de dados. | ||
<java5> | |||
public interface DisplayElement { | |||
public void display(); | |||
} | } | ||
</java5> | |||
As implementações da interface de apresentação, que implementam também a de observação, definem várias formas de exibição de dados. | As implementações da interface de apresentação, que implementam também a de observação, definem várias formas de exibição de dados. | ||
<java5> | |||
public class CurrentConditionsDisplay implements Observer, DisplayElement { | |||
private float _temperature; | |||
private float _humidity; | |||
private Subject _weatherData; | |||
public CurrentConditionsDisplay(Subject weatherData) { | |||
_weatherData = weatherData; | |||
_weatherData.registerObserver(this); | |||
} | } | ||
public void update(float temperature, float humidity, float pressure) { | |||
_temperature = temperature; | |||
_humidity = humidity; | |||
display(); | |||
} | } | ||
public void display() { | |||
System.out.println("Current conditions: " + _temperature + "F degrees and " + _humidity + "% humidity"); | |||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
</java5> | |||
<java5> | |||
public class ForecastDisplay implements Observer, DisplayElement { | |||
private float _currentPressure = 29.92f; | |||
private float _lastPressure; | |||
private WeatherData _weatherData; | |||
public ForecastDisplay(WeatherData weatherData) { | |||
_weatherData = weatherData; | |||
_weatherData.registerObserver(this); | |||
} | } | ||
public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure) { | |||
_lastPressure = currentPressure; | |||
_currentPressure = pressure; | |||
display(); | |||
} | } | ||
public void display() { | |||
System.out.print("Forecast: "); | |||
if (_currentPressure > _lastPressure) { | |||
System.out.println("Improving weather on the way!"); | |||
} | } else if (_currentPressure == _lastPressure) { | ||
System.out.println("More of the same"); | |||
} | } else if (_currentPressure < _lastPressure) { | ||
System.out.println("Watch out for cooler, rainy weather"); | |||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
</java5> | |||
===Representação de dados=== | ===Representação de dados=== | ||
| Line 96: | Line 105: | ||
Os dados de meteorologia correspondem ao objecto observado. | Os dados de meteorologia correspondem ao objecto observado. | ||
< | <java5> | ||
public class WeatherData implements Subject { | public class WeatherData implements Subject { | ||
private ArrayList<Observer> _observers = new ArrayList<Observer>(); | private ArrayList<Observer> _observers = new ArrayList<Observer>(); | ||
| Line 129: | Line 138: | ||
} | } | ||
</ | </java5> | ||
===Dois contextos=== | ===Dois contextos=== | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 19 November 2008
O padrão observer permite observar o estado de um objecto. Os observadores registam o seu interesse no estado junto do objecto; quando o estado do objecto muda, os observadores são notificados.
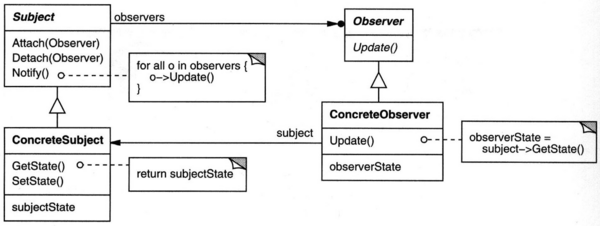
Estrutura
Diagrama de classes
O padrão observer tem a seguinte estrutura de classes:
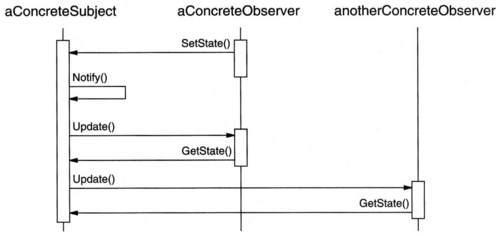
Diagrama de sequência
As colaborações entre os intervenientes são as que figuram no seguinte diagrama de sequência:
Exemplo
Observadores e Observados
<java5>
public interface Subject {
public void registerObserver(Observer o);
public void removeObserver(Observer o);
public void notifyObservers();
}
</java5>
<java5>
public interface Observer {
public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure);
}
</java5>
Apresentação
Esta interface define o método básico para apresentação de dados.
<java5>
public interface DisplayElement {
public void display();
}
</java5>
As implementações da interface de apresentação, que implementam também a de observação, definem várias formas de exibição de dados.
<java5>
public class CurrentConditionsDisplay implements Observer, DisplayElement {
private float _temperature;
private float _humidity;
private Subject _weatherData;
public CurrentConditionsDisplay(Subject weatherData) {
_weatherData = weatherData;
_weatherData.registerObserver(this);
}
public void update(float temperature, float humidity, float pressure) {
_temperature = temperature;
_humidity = humidity;
display();
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Current conditions: " + _temperature + "F degrees and " + _humidity + "% humidity");
}
}
</java5>
<java5>
public class ForecastDisplay implements Observer, DisplayElement {
private float _currentPressure = 29.92f;
private float _lastPressure;
private WeatherData _weatherData;
public ForecastDisplay(WeatherData weatherData) {
_weatherData = weatherData;
_weatherData.registerObserver(this);
}
public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure) {
_lastPressure = currentPressure;
_currentPressure = pressure;
display();
}
public void display() {
System.out.print("Forecast: ");
if (_currentPressure > _lastPressure) {
System.out.println("Improving weather on the way!");
} else if (_currentPressure == _lastPressure) {
System.out.println("More of the same");
} else if (_currentPressure < _lastPressure) {
System.out.println("Watch out for cooler, rainy weather");
}
}
}
</java5>
Representação de dados
Os dados de meteorologia correspondem ao objecto observado.
<java5>
public class WeatherData implements Subject {
private ArrayList<Observer> _observers = new ArrayList<Observer>();
private float _temperature;
private float _humidity;
private float _pressure;
public WeatherData() { }
public void registerObserver(Observer o) { _observers.add(o); }
public void removeObserver(Observer o) {
int i = _observers.indexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) { _observers.remove(i); }
}
public void notifyObservers() {
for (int i = 0; i < _observers.size(); i++) {
Observer observer = _observers.get(i);
observer.update(temperature, humidity, pressure);
}
}
public void measurementsChanged() { notifyObservers(); }
public void setMeasurements(float temperature, float humidity, float pressure) {
_temperature = temperature;
_humidity = humidity;
_pressure = pressure;
measurementsChanged();
}
}
</java5>
Dois contextos
Os dois contextos de utilização correspondem a duas estações meteorológicas: em cada uma são utilizados observadores diferentes sobre os mesmos dados.
public class WeatherStation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeatherData weatherData = new WeatherData();
CurrentConditionsDisplay currentDisplay = new CurrentConditionsDisplay(weatherData);
StatisticsDisplay statisticsDisplay = new StatisticsDisplay(weatherData);
ForecastDisplay forecastDisplay = new ForecastDisplay(weatherData);
weatherData.setMeasurements(80, 65, 30.4f);
weatherData.setMeasurements(82, 70, 29.2f);
weatherData.setMeasurements(78, 90, 29.2f);
}
}
public class WeatherStationHeatIndex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeatherData weatherData = new WeatherData();
CurrentConditionsDisplay currentDisplay = new CurrentConditionsDisplay(weatherData);
StatisticsDisplay statisticsDisplay = new StatisticsDisplay(weatherData);
ForecastDisplay forecastDisplay = new ForecastDisplay(weatherData);
HeatIndexDisplay heatIndexDisplay = new HeatIndexDisplay(weatherData);
weatherData.setMeasurements(80, 65, 30.4f);
weatherData.setMeasurements(82, 70, 29.2f);
weatherData.setMeasurements(78, 90, 29.2f);
}
}