Bottom-Up Parsing/Exercise 9: LALR(1): Difference between revisions
From Wiki**3
Created page with "== Problema == Consider the following grammar, where E is the initial symbol and { [, ], ;, id } is the set of terminal symbols: <text> E -> [ E ; L ] | id L -> E | E ; L </..." |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Problema == | == Problema == | ||
Consider the following grammar, where E is the initial symbol and { [, ], ;, id } is the set of terminal symbols: | Consider the following grammar, where '''E''' is the initial symbol and '''{ [, ], ;, id }''' is the set of terminal symbols: | ||
<text> | <source lang="text"> | ||
E | E → [ E ; L ] | id | ||
L | L → E | E ; L | ||
</ | </source> | ||
# Compute the set of LALR(1) states for the grammar. Build the corresponding LALR(1) parse table. | # Compute the set of LALR(1) states for the grammar. Build the corresponding LALR(1) parse table. | ||
# Show the parsing process for input '''[id;id;id]''' (including the actions/gotos and the input and stack states). In case of conflict, assume YACC's behavior. | # Show the parsing process for input '''[id;id;id]''' (including the actions/gotos and the input and stack states). In case of conflict, assume YACC's behavior. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Solução == | == Solução == | ||
{{CollapsedCode|Solução completa| | |||
[[image:eobesclcb.png]] | |||
}} | |||
[[category:Compiladores]] | [[category:Compiladores]] | ||
[[category:Ensino]] | [[category:Ensino]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:49, 2 May 2024
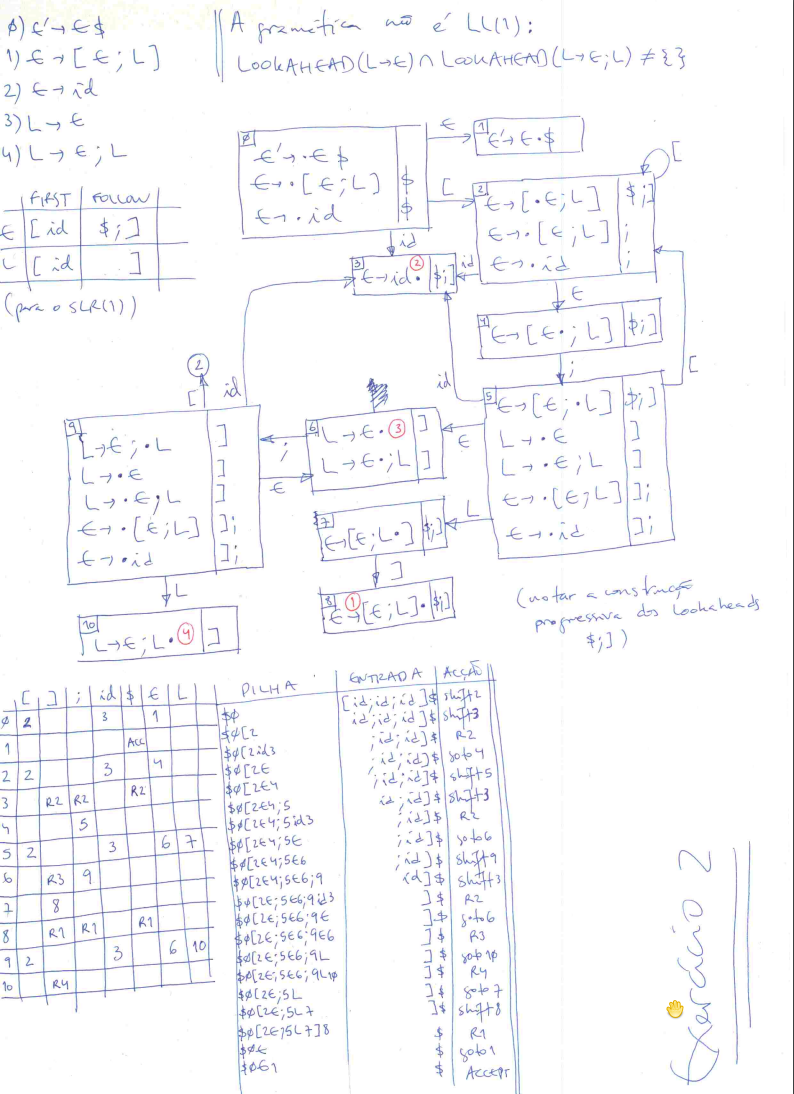
Problema
Consider the following grammar, where E is the initial symbol and { [, ], ;, id } is the set of terminal symbols:
E → [ E ; L ] | id
L → E | E ; L
- Compute the set of LALR(1) states for the grammar. Build the corresponding LALR(1) parse table.
- Show the parsing process for input [id;id;id] (including the actions/gotos and the input and stack states). In case of conflict, assume YACC's behavior.
- Is this an LL(1) grammar? Why?
Solução
| Solução completa |
|---|