Top-Down Parsing/Exercise 7: Difference between revisions
From Wiki**3
No edit summary |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
X -> a | X -> a | ||
A -> X c A e | M b | A -> X c A e | M b | ||
M -> A c | X c d | | M -> A c | X c d | ε | ||
# Examine the grammar and rewrite it so that an LL(1) predictive parser can be built for the corresponding language. | # Examine the grammar and rewrite it so that an LL(1) predictive parser can be built for the corresponding language. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[Image:CompilersTopDownParsingExercise7.jpg|700px]] | [[Image:CompilersTopDownParsingExercise7.jpg|700px]] | ||
[[category:Compiladores]] | |||
[[category: | [[category:Ensino]] | ||
[[category: | |||
Latest revision as of 14:04, 30 April 2024
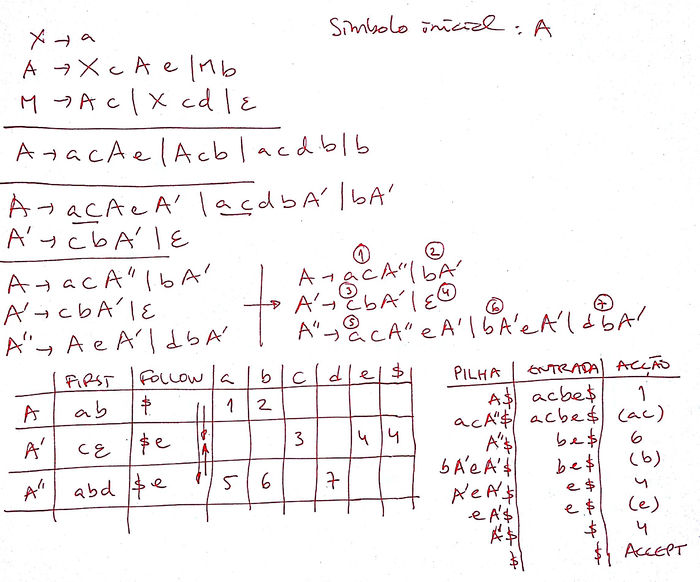
Problem
Consider the following grammar, where A is the initial symbol and {a,b,c,d,e} is the set of terminal symbols:
X -> a A -> X c A e | M b M -> A c | X c d | ε
- Examine the grammar and rewrite it so that an LL(1) predictive parser can be built for the corresponding language.
- Compute the FIRST and FOLLOW sets for all non-terminal symbols in the new grammar and build the parse table.
- Show the analysis table (stack, input, and actions) for the parsing process of the acbe input sequence.