Bottom-Up Parsing/Exercise 12: LALR(1): Difference between revisions
From Wiki**3
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Consider the following grammar, where A is the initial symbol and { x, y, z } is the set of terminal symbols: | Consider the following grammar, where A is the initial symbol and { x, y, z } is the set of terminal symbols: | ||
<text> | <source lang="text"> | ||
A -> B x y | x y x | x B y | A -> B x y | x y x | x B y | ||
B -> z | ε | B -> z | ε | ||
</ | </source> | ||
# Compute the set of LALR(1) states for the grammar. Build the corresponding LALR(1) parse table. | # Compute the set of LALR(1) states for the grammar. Build the corresponding LALR(1) parse table. | ||
# Compact the parse table, eliminating and propagating reductions. | # Compact the parse table, eliminating and propagating reductions. | ||
Revision as of 11:27, 12 February 2019
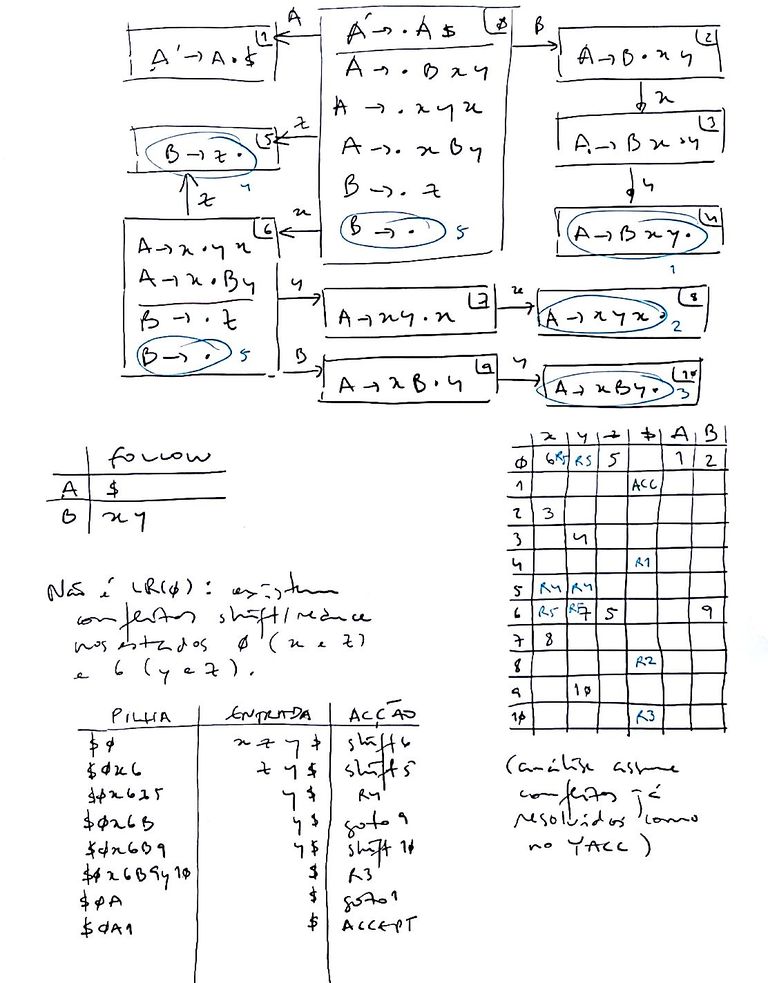
Problema
Consider the following grammar, where A is the initial symbol and { x, y, z } is the set of terminal symbols:
A -> B x y | x y x | x B y
B -> z | ε
- Compute the set of LALR(1) states for the grammar. Build the corresponding LALR(1) parse table.
- Compact the parse table, eliminating and propagating reductions.
- Show the parsing process for input xzy (including the actions/gotos and the input and stack states). In case of conflict, assume YACC's behavior.
Solução
| Solução (sem compactação) para SLR(1) |
|---|
| Solução completa para LALR(1) |
|---|