Difference between revisions of "Decorator Pattern (padrão de desenho)/Exercício 1: Textos Formatados"
From Wiki**3
< Decorator Pattern (padrão de desenho)
(→Class TextSpan) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
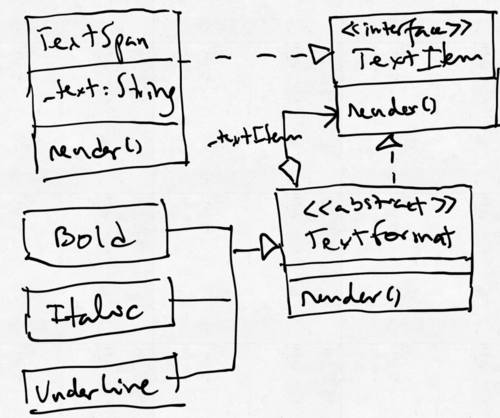
Este diagrama corresponde às classes abaixo definidas. Note-se queo método render está declarado em todas as classes. Não foi representado em algumas por simplicidade. | Este diagrama corresponde às classes abaixo definidas. Note-se queo método render está declarado em todas as classes. Não foi representado em algumas por simplicidade. | ||
| + | {{CollapsedCode|Diagrama de classes| | ||
[[Image:decorator-ex1.png|500px]] | [[Image:decorator-ex1.png|500px]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
== Interface TextItem == | == Interface TextItem == | ||
| Line 27: | Line 29: | ||
Esta interface representa um item textual genérico, formatado ou não. | Esta interface representa um item textual genérico, formatado ou não. | ||
| − | < | + | {{CollapsedCode|Ficheiro '''TextItem.java'''| |
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
public interface TextItem { | public interface TextItem { | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * Text items can be rendered. | |
| − | + | * | |
| − | + | * @return rendered text item. | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | String render(); | |
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| + | }} | ||
== Class TextSpan == | == Class TextSpan == | ||
A text span contains some text. | A text span contains some text. | ||
| − | < | + | {{CollapsedCode|Ficheiro '''TextSpan.java'''| |
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
public class TextSpan implements TextItem { | public class TextSpan implements TextItem { | ||
| − | + | /** The text in this span. */ | |
| − | + | private String _text; | |
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @param text | |
| − | + | * the text in this span. | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | public TextSpan(String text) { | |
| − | + | _text = text; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @see TextItem#render() | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | @Override | |
| − | + | public String render() { | |
| − | + | return "<span>" + _text + "</span>"; | |
| − | + | } | |
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| + | }} | ||
== Class TextFormat == | == Class TextFormat == | ||
| − | The abstract format (root class for other formatting items). | + | The abstract format (root class for other formatting items). A text format may be applied to any text item. |
| − | < | + | {{CollapsedCode|Ficheiro '''TextFormat.java'''| |
| − | + | <source lang="java"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
public abstract class TextFormat implements TextItem { | public abstract class TextFormat implements TextItem { | ||
| − | + | /** The text item to format. */ | |
| − | + | private TextItem _textItem; | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @param textItem | |
| − | + | * the text item to format. | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | public TextFormat(TextItem textItem) { | |
| − | + | _textItem = textItem; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @return the text item. | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | public TextItem getTextItem() { | |
| − | + | return _textItem; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * Subclasses will do the rest. | |
| − | + | * | |
| − | + | * @see TextItem#render() | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | public String render() { | |
| − | + | return _textItem.render(); | |
| − | + | } | |
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| + | }} | ||
== Class Bold == | == Class Bold == | ||
| − | + | Bold format. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {{CollapsedCode|Ficheiro '''Bold.java'''| | |
| − | + | <source lang="java"> | |
public class Bold extends TextFormat { | public class Bold extends TextFormat { | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @param textItem the text item to format. | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | public Bold(TextItem textItem) { | |
| − | + | super(textItem); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @see TextItem#render() | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | @Override | |
| − | + | public String render() { | |
| − | + | return "<b>" + super.render() + "</b>"; | |
| − | + | } | |
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| + | }} | ||
== Class Italic == | == Class Italic == | ||
| − | + | Italic format. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {{CollapsedCode|Ficheiro '''Italic.java'''| | |
| − | + | <source lang="java"> | |
public class Italic extends TextFormat { | public class Italic extends TextFormat { | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @param textItem the text item to format. | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | public Italic(TextItem textItem) { | |
| − | + | super(textItem); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @see TextItem#render() | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | @Override | |
| − | + | public String render() { | |
| − | + | return "<i>" + super.render() + "</i>"; | |
| − | + | } | |
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| + | }} | ||
== Class Underline == | == Class Underline == | ||
| − | + | Underline format. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {{CollapsedCode|Ficheiro '''Underline.java'''| | |
| − | + | <source lang="java"> | |
public class Underline extends TextFormat { | public class Underline extends TextFormat { | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @param textItem the text item to format. | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | public Underline(TextItem textItem) { | |
| − | + | super(textItem); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @see TextItem#render() | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | @Override | |
| − | + | public String render() { | |
| − | + | return "<u>" + super.render() + "</u>"; | |
| − | + | } | |
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| + | }} | ||
== Class App == | == Class App == | ||
| Line 190: | Line 196: | ||
Simple demo application. | Simple demo application. | ||
| − | < | + | {{CollapsedCode|Ficheiro '''App.java'''| |
| − | + | <source lang="java"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
public class App { | public class App { | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * @param args | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | public static void main(String[] args) { | |
| − | + | TextItem span1 = new TextSpan("BATATA"); | |
| − | + | TextItem text1 = new Bold(new Italic(span1)); | |
| − | + | System.out.println(text1.render()); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | TextItem span2 = new TextSpan("CEBOLA"); | |
| − | + | TextItem text2 = new Underline(new Bold(new Italic(span2))); | |
| − | + | System.out.println(text2.render()); | |
| − | + | } | |
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| + | }} | ||
= Compiling and Running = | = Compiling and Running = | ||
Latest revision as of 20:50, 8 November 2018
Problema
Um texto é constituído por palavras. Quando o texto é apresentado, através do método render, cada palavra pode aparecer sem qualquer modificação de aspecto (utiliza-se o método render correspondente). É ainda possível modificar dinamicamente o aspecto das palavras, permitindo que sejam apresentadas em negrito, itálico, sublinhado, ou em combinações variadas (e.g. negrito e itálico ou itálico sublinhado, etc.). No entanto, a apresentação é sempre realizada da mesma forma (sempre através do método render).
Além de apresentável graficamente, um texto pode ser convertido numa cadeia de caracteres, contendo a sua informação textual (String). Esta operação é realizada através do método text (invocado sobre cada um dos elementos designados acima).
Implemente as classes que permitem representar o texto completo, as palavras, respectivas modificações gráficas. Implemente ainda uma aplicação que ilustre o comportamento. Represente as características gráficas da seguinte forma:
- normal <span>normal</span>
- negrito <b>negrito</b>
- itálico <i>itálico</i>
- sublinhado <u>sublinhado</u>
Solução
A solução apresentada abaixo não contempla o método text. Deixa-se como exercício para o leitor.
Diagrama UML
Este diagrama corresponde às classes abaixo definidas. Note-se queo método render está declarado em todas as classes. Não foi representado em algumas por simplicidade.
| Diagrama de classes |
|---|
Interface TextItem
Esta interface representa um item textual genérico, formatado ou não.
| Ficheiro TextItem.java |
|---|
public interface TextItem {
/**
* Text items can be rendered.
*
* @return rendered text item.
*/
String render();
}
|
Class TextSpan
A text span contains some text.
| Ficheiro TextSpan.java |
|---|
public class TextSpan implements TextItem {
/** The text in this span. */
private String _text;
/**
* @param text
* the text in this span.
*/
public TextSpan(String text) {
_text = text;
}
/**
* @see TextItem#render()
*/
@Override
public String render() {
return "<span>" + _text + "</span>";
}
}
|
Class TextFormat
The abstract format (root class for other formatting items). A text format may be applied to any text item.
| Ficheiro TextFormat.java |
|---|
public abstract class TextFormat implements TextItem {
/** The text item to format. */
private TextItem _textItem;
/**
* @param textItem
* the text item to format.
*/
public TextFormat(TextItem textItem) {
_textItem = textItem;
}
/**
* @return the text item.
*/
public TextItem getTextItem() {
return _textItem;
}
/**
* Subclasses will do the rest.
*
* @see TextItem#render()
*/
public String render() {
return _textItem.render();
}
}
|
Class Bold
Bold format.
| Ficheiro Bold.java |
|---|
public class Bold extends TextFormat {
/**
* @param textItem the text item to format.
*/
public Bold(TextItem textItem) {
super(textItem);
}
/**
* @see TextItem#render()
*/
@Override
public String render() {
return "<b>" + super.render() + "</b>";
}
}
|
Class Italic
Italic format.
| Ficheiro Italic.java |
|---|
public class Italic extends TextFormat {
/**
* @param textItem the text item to format.
*/
public Italic(TextItem textItem) {
super(textItem);
}
/**
* @see TextItem#render()
*/
@Override
public String render() {
return "<i>" + super.render() + "</i>";
}
}
|
Class Underline
Underline format.
| Ficheiro Underline.java |
|---|
public class Underline extends TextFormat {
/**
* @param textItem the text item to format.
*/
public Underline(TextItem textItem) {
super(textItem);
}
/**
* @see TextItem#render()
*/
@Override
public String render() {
return "<u>" + super.render() + "</u>";
}
}
|
Class App
Simple demo application.
| Ficheiro App.java |
|---|
public class App {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
TextItem span1 = new TextSpan("BATATA");
TextItem text1 = new Bold(new Italic(span1));
System.out.println(text1.render());
TextItem span2 = new TextSpan("CEBOLA");
TextItem text2 = new Underline(new Bold(new Italic(span2)));
System.out.println(text2.render());
}
}
|